What is Solar Energy and How Does it Work?
Solar energy is becoming increasingly important in our world today. This renewable resource harnesses sunlight to produce electricity and heat. Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in solar energy, once stated, "Solar power is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for a sustainable future."
The technology behind solar energy is fascinating. Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity. This process involves complex materials, yet the concept is simple: capture sunlight. Many households are now installing solar panels. However, the initial costs can be daunting, and not everyone has access.
Moreover, there are challenges in storage and efficiency. Current solar technology isn’t perfect. Some areas receive less sunlight, reducing its effectiveness. Not every innovation has lived up to its promise. Yet, the potential of solar energy is undeniable. It offers a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. There is still much to learn, adapt, and improve in this field.

What is Solar Energy? A Definition and Overview
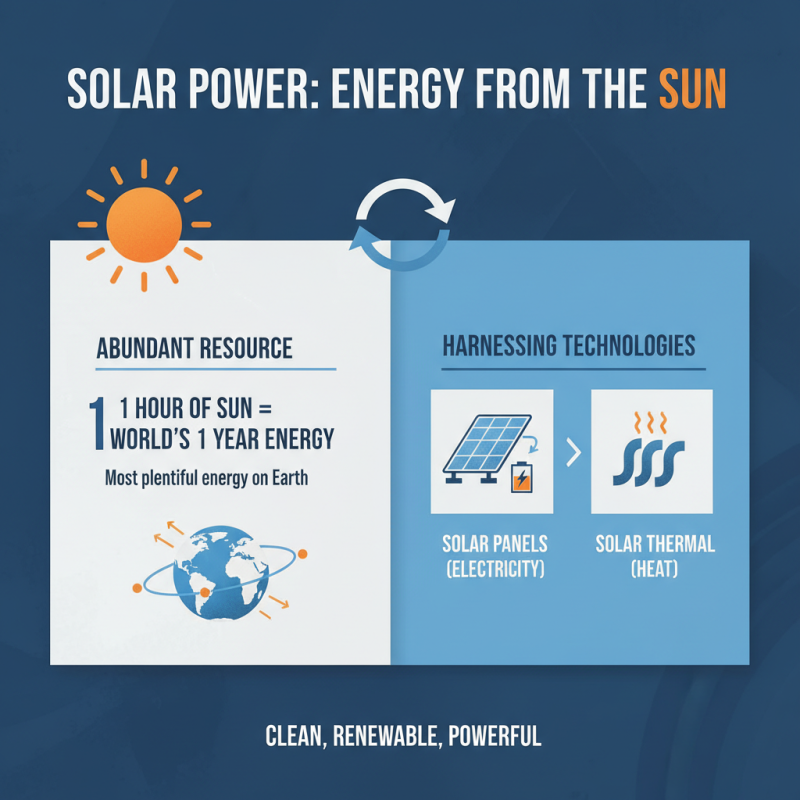
Solar energy is a powerful and renewable resource harnessed from the sun's rays. It is perhaps one of the most abundant forms of energy available on Earth. Every hour, the sun emits more energy than the entire world uses in one year. This energy can be captured through various technologies, mainly solar panels and solar thermal systems.
When sunlight hits solar panels, they convert this light into electricity. This process involves the photovoltaic effect, where certain materials generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight. Conversely, solar thermal systems use sunlight to produce heat. These systems are employed for heating water or spaces in homes. However, solar technology is not without its challenges.
The effectiveness of solar energy can be hindered by weather conditions. Cloudy days can significantly reduce energy production. Additionally, the initial cost of installing solar systems can be high, which makes some homeowners hesitant. Space requirements for solar panels can also pose a challenge for urban dwellers. Despite these hurdles, the increasing emphasis on sustainable energy makes solar a crucial player in the future energy landscape.
The Science Behind Solar Energy: Photovoltaic Effect Explained
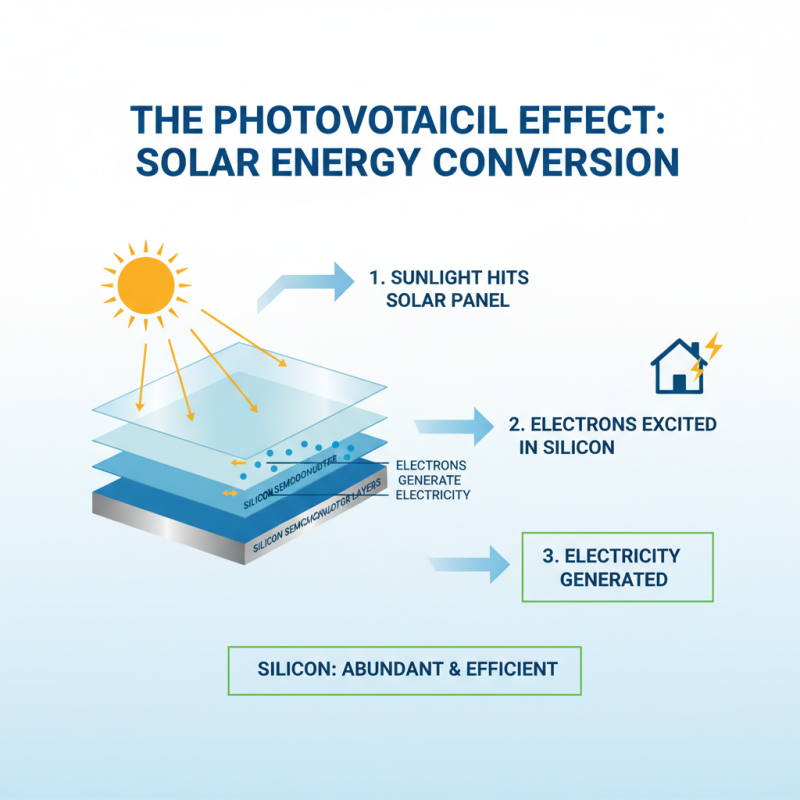
The photovoltaic effect is the key mechanism behind solar energy conversion. When sunlight hits a solar panel, it excites electrons within semiconductor materials, generating electricity. This process occurs within thin layers of silicon, which are abundant and effective for energy transformation.
Solar cells capture sunlight and convert it into usable energy. However, not all panels perform equally. Factors like temperature and angle can affect efficiency. If panels are too hot, their performance diminishes. Regular cleaning of dust and debris is also crucial for optimal function.
Tips: When installing solar panels, consider their orientation. A south-facing angle maximizes sun exposure. Assess your local climate too. Areas with regular sun are ideal for solar energy solutions, while cloudy regions may struggle to see significant benefits. Remember, even imperfect installations can yield results—just not as high as expected.
Types of Solar Energy Systems: Active vs. Passive Solar Technologies
Active and passive solar energy systems serve different purposes. Active solar technologies use mechanical or electrical devices to convert sunlight into usable energy. Solar panels, for instance, capture sunlight and transform it into electricity. This process often requires an inverter that changes direct current into alternating current for home use. While these systems can generate significant power, they rely heavily on technology. This dependence creates additional costs and complexity.
Passive solar technologies focus on design and placement. They utilize natural materials and building orientation to enhance energy efficiency. For example, large south-facing windows can capture sunlight to heat rooms. Overhangs can block excessive summer heat while allowing winter sunlight to warm the space. This method is less reliant on complex systems, but it requires careful planning. The challenge lies in achieving the right balance between window sizes and shading devices.
Both systems have their merits and drawbacks. Active systems can produce more energy but might generate waste when the sun isn't shining. Passive systems are energy-efficient but may not meet all energy demands. As we explore solar technologies, reflecting on these trade-offs becomes vital for effective implementation. Consider how your choices impact energy consumption and sustainability.
Solar Energy Production by Type (2022)
Global Solar Energy Market Growth: Statistics and Future Projections
The global solar energy market is experiencing rapid growth. In recent years, solar capacity has surged, driven by decreasing costs and technological advancements. Analysts forecast that by 2030, the solar market could reach an impressive value, supporting a cleaner energy future worldwide.
As more countries adopt solar energy, the statistics are promising. In 2022 alone, solar installations increased significantly in regions that traditionally relied on fossil fuels.
Emerging markets show great potential, but some face challenges, such as infrastructure and investment barriers.
Tips: Consider local incentives for solar energy installation. Engaging with community programs can also provide resources and support. Exploring government grants may ease the financial burden for new solar projects. Despite the exciting growth, it's essential to recognize that not all installations meet sustainability goals. Balancing economic growth with environmental impact remains a critical challenge in this fast-evolving landscape.
Environmental Impact of Solar Energy: Benefits and Challenges
Solar energy has gained popularity due to its potential environmental benefits. It generates electricity without depleting natural resources. Solar panels convert sunlight into energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions, which is vital for combating climate change.
However, there are challenges to consider. The production of solar panels involves mining for raw materials. This process can harm ecosystems. Additionally, the recycling of old panels poses a problem. Not all regions have adequate methods for disposal. Therefore, while solar energy is cleaner, its entire lifecycle needs careful evaluation.
Another aspect is land use. Large solar farms require vast areas, which sometimes leads to habitat loss. This can threaten local wildlife. Balancing solar energy production with environmental conservation is complex. We must continue to seek ways to optimize solar technology. Finding solutions to these concerns is essential for truly sustainable energy use.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future: How Solar Solutions Are Transforming Energy Consumption in Urban Areas
-

How to Choose the Best Solar Electricity System for Your Home
-

Harnessing Solar Energy System for a Sustainable Future and Reduced Energy Bills
-

How to Maximize Your Savings: The Ultimate Guide to Solar Panel Energy Efficiency
-

How to Maximize Your Savings with Solar Panel Energy in 2025
-

How to Choose the Right Solar Energy System for Your Home in 2025
