How to Choose the Best Solar Technology for Your Home Energy Needs
Choosing the right solar technology for your home can be a transformative decision that significantly impacts your energy consumption and sustainability efforts. According to Dr. Emily Hart, a leading expert in renewable energy systems, "The key to maximizing your home’s energy efficiency lies in selecting the solar technology that best aligns with your specific needs and lifestyle." With the rapid advancements in solar technology, homeowners are presented with a range of options, from photovoltaic cells to solar thermal systems, each offering unique benefits tailored to various energy demands.
Understanding the nuances of these technologies is crucial as they each come with their own set of efficiencies, costs, and installation requirements. Dr. Hart emphasizes that "the right choice can lead to substantial savings on energy bills while contributing to a greener planet." In this context, careful evaluation of your energy needs, budget, and future goals will guide you in making an informed decision. This guide aims to illuminate the factors to consider when choosing solar technology, ensuring you harness the full potential of solar energy in your home.

Understanding Different Solar Technology Types for Home Use
When considering the best solar technology for your home energy needs, it's crucial to understand the various types of solar technologies available. The primary types include photovoltaic (PV) systems, solar thermal systems, and concentrated solar power (CSP). PV systems, which convert sunlight directly into electricity, are widely favored by homeowners due to their relatively low maintenance and ease of installation. According to a recent report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the cost of residential PV systems has dropped by nearly 70% since 2010, making them more accessible for homeowners looking to reduce energy bills and carbon footprints.
Solar thermal systems, on the other hand, are designed to collect and convert sunlight into heat, which can be used for water heating or space heating. This technology is particularly effective in regions with high direct sunlight and can significantly reduce utility costs. A study by the U.S. Department of Energy highlighted that solar thermal systems could save up to 30-50% on water heating bills, depending on local climate conditions and household energy consumption patterns. Meanwhile, CSP technology, while primarily used in large-scale solar power plants, is gaining attention for potential residential applications due to advances in energy storage capabilities, which allow for power generation even when sunlight is not available.
Ultimately, choosing the best solar technology involves evaluating your specific energy needs, local climate, and budget. Understanding these different solar technologies helps homeowners make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and financial objectives.
Solar Technology Types Comparison
Evaluating Your Home's Energy Needs and Consumption Patterns
When considering solar technology for your home, evaluating your energy needs and consumption patterns is crucial. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average American household consumes about 877 kWh per month. This figure can be influenced by various factors including the size of your home, the number of occupants, and your lifestyle choices. Analyzing your electric bills can provide insights into peak usage times and areas where energy efficiency improvements can be made.
It is essential to track your historical energy consumption to accurately estimate your future needs, especially if you plan to add new appliances or make improvements to your home.
Another important aspect to consider is how domestic energy consumption varies with seasons and weather. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reports that energy use can increase significantly during summer months due to air conditioning, while winter months may see higher energy demands for heating. By understanding these patterns, homeowners can better decide on the size and type of solar system that would be most effective.
A well-designed solar energy system should align with your peak consumption periods, ensuring that it can deliver maximum efficiency and savings over time. Taking the time to assess these factors will pave the way for a more informed decision when selecting the best solar technology for your home energy needs.
Comparing Efficiency Ratings of Solar Panels and Their Impact on Choice
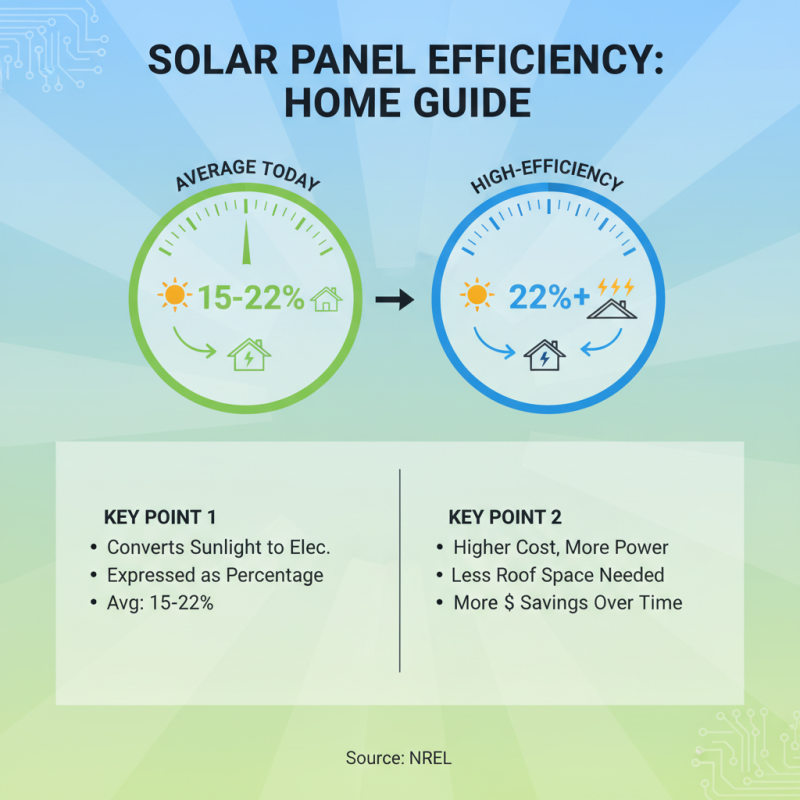
When choosing the best solar technology for your home, one of the critical factors to consider is the efficiency rating of solar panels. Efficiency measures how well a solar panel converts sunlight into usable electricity, typically expressed as a percentage. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), the average efficiency of commercially available solar panels ranges from 15% to 22%, with higher efficiency panels often corresponding to a higher initial investment. However, these high-efficiency models can produce more electricity per square foot, making them an attractive choice for homeowners with limited roof space.
In addition to efficiency ratings, it’s essential to consider how these ratings impact overall energy needs and costs. A report from the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) suggests that for residential installations, the difference in efficiency can lead to substantial variations in energy production over time. Higher-efficiency panels may yield roughly 20-30% more energy over their lifespan compared to lower efficiency options. This increased output can significantly offset installation costs over time, making it crucial for homeowners to assess their specific energy requirements in conjunction with panel efficiency. Careful consideration of these factors can lead to more informed decisions that align with both financial and environmental goals.
Assessing Installation Costs and Financial Incentives for Solar Technologies
When considering solar technology for your home, a crucial aspect is understanding installation costs and available financial incentives. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), the average cost of solar panel installations has decreased significantly, dropping approximately 70% since 2010. This trend signifies that more homeowners can consider solar energy as a viable option for their energy needs. However, installation prices can still vary widely based on factors like system size, roof type, and regional labor costs. Homeowners should get multiple quotes from local installers to ensure they are receiving a competitive price.
In addition to installation costs, financial incentives can significantly affect the overall affordability of solar installations. Many states offer tax credits, rebates, and other incentives to make solar energy more accessible. For instance, the federal solar investment tax credit (ITC) allows homeowners to deduct a substantial percentage of their solar system costs from their federal taxes. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, states like California and New York also provide generous local incentives that can lead to further savings. It’s vital for homeowners to research available programs in their area to maximize their financial benefits.
Tips for maximizing your solar investment include checking your eligibility for net metering programs, which can credit you for excess energy sent back to the grid, and investing in energy-efficient appliances that can reduce your overall energy consumption. Additionally, consider conducting a home energy audit to identify areas where you can improve efficiency before installing solar technology. Doing so can ensure that your solar system meets your energy needs effectively while optimizing your financial returns.
Analyzing Long-Term Return on Investment for Residential Solar Solutions
When considering the long-term return on investment (ROI) for residential solar solutions, it is crucial to analyze various factors that contribute to both the savings and initial costs associated with installation. Primarily, homeowners should evaluate the energy needs of their household and how a solar system can meet these requirements. By estimating potential energy production, based on roof orientation and local climate, homeowners can determine how much energy expense can be offset. Additionally, assessing local electricity rates and projected increases can provide insights into the cost savings over time.
Another integral aspect of analyzing ROI is understanding the financial incentives available. Many regions offer tax credits, rebates, or other financial programs that can significantly lower the upfront costs of solar installation. Evaluating these incentives alongside the typical lifespan of solar panels, which is generally around 25 years, helps homeowners make informed decisions about how quickly they can recoup their initial investment.
It’s also essential to consider maintenance costs and the potential for increased property value, as these factors can further enhance the return on investment over the years. Balancing these elements will ultimately guide homeowners to the best solar technology suited for their energy needs while ensuring financial viability.
Related Posts
-

Harnessing Solar Panel Energy Trends at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

How to Maximize Your Energy Savings with Innovative Solar Solutions
-

Transform Your Home: The Ultimate Guide to Solar Electricity Systems and Their Benefits
-

Harnessing Solar Energy System for a Sustainable Future and Reduced Energy Bills
-

2025 Top 5 Innovations in Solar Technology You Need to Know About
-

Understanding Solar Panel Efficiency: How to Maximize Energy Output
